The latest quarterly results from Samsung fell short of expectations as the company tries to claw its way into the profitable high-bandwidth memory (HBM) market where SK hynix has a commanding lead, followed by Micron.
HBM stacks layers of DRAM on top of an interposer to create memory products that are connected to GPUs, providing faster bandwidth and higher capacity than the socket-connected memory used by x86 processors. HBM memory costs more than ordinary DRAM and SK hynix and Micron revenues are soaring as demand for high-bandwidth GPU memory goes up in lockstep with AI application use. In November, SK hynix added four more layers to its 12-Hi HBM3e memory chips to increase capacity from 36 to 48 GB and is set to sample this 16-Hi product this year. The faster HBM4 standard should arrive this year as well, with a stack bandwidth of around 1.5 TBps compared to HBM3e’s 1.2-plus TBps.
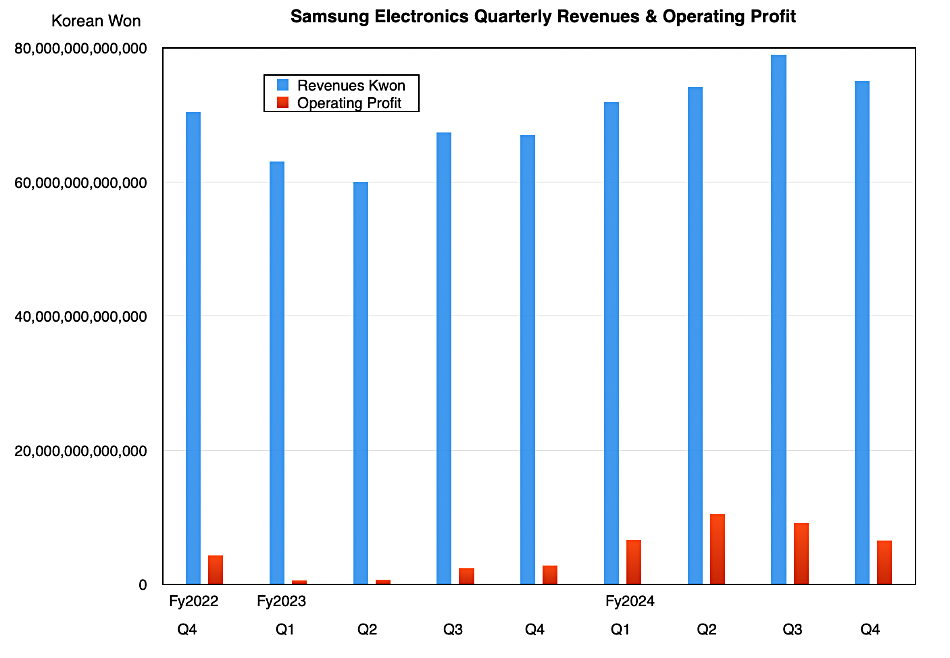
Samsung filed preliminary figures for the quarter ended December 31, with ₩75 trillion ($51.4 billion) in revenues, up 10.7 percent annually but below analyst estimates, and ₩6.5 trillion ($4.5 billion) operating profit, lower than the forecast ₩8.96 trillion ($6.1 billion) and 30 percent less than the prior quarter.
Management said: “Our operating profit for 4Q24 is projected to come in significantly below market expectations. This explanatory note is provided to assist in the understanding of the key factors behind the results and alleviate uncertainties prior to the release of our full results in the 4Q24 earnings call.”
“Despite sluggish demand for conventional PC and mobile-focused products, revenue in the Memory business reached a new all-time high for the fourth quarter, driven by strong sales of high-density products. However, Memory operating profit declined, weighed on by increased R&D expenses aimed at securing future technology leadership and the initial ramp-up costs tied to expanding production capacity for advanced technologies.”
TrendForce analyst Eden Chung told AFP he believes that Samsung Foundry faces multiple challenges, including “order losses from key customers in advanced processes, the gradual end-of-life of certain products, and a slow recovery in mature process segments.”
Manufacturing HBM chips is more profitable than traditional DRAM. Once GPU market leader Nvidia qualifies a manufacturer’s HBM product, sales take off. Samsung has fallen behind SK hynix and Micron in getting its latest HBM chips qualified by Nvidia. The company replaced its semiconductor unit’s leadership in November as it responded to slow memory chip sales, the second such exec reshuffle that year. A month earlier, the company had acknowledged it was in crisis and there were concerns about its technology’s competitiveness.
Mobile phone memory demand is relatively weak and domestic DRAM suppliers in China are taking a larger proportion of memory sales there.
According to Reuters, Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang told reporters at CES that Samsung is working on a new HBM chip design and he was confident that Samsung could succeed in this project.










